Melamine is an organic compound that has historically appeared as an illegal additive in food and feed. However, it can also unintentionally enter food through food contact materials such as plastic items, can linings, paper, cardboard and adhesives. It is also a degradation product of cyromazine, which is used as a pesticide, veterinary medicine and flame retardant, and may be present as a contaminant through this route.
Melamine with the chemical formula C3H6N6 has a percentage nitrogen content of 66.6 %, which is significantly higher than that of most foods, which contain 2 to 5 % nitrogen. The protein content is calculated via the measured nitrogen content. For this reason, it has been used fraudulently to adulterate foods by faking a higher protein content in the product.
In 2010, EFSA published a scientific opinion on melamine in food and feed. The results of this opinion show that exposure to melamine or its degradation product cyanuric acid can lead to the formation of kidney stones. The crystals cause injuries to the proximal tubules. Thousands of children fell ill in China and several infants died after eating milk formula adulterated with melamine. For this reason, melamine was included in Regulation (EC) 1881/2006 and a maximum limit of 2.5 mg/kg was set for all types of food. A maximum value of 1 mg/kg applies to powdered infant food and derived products. Directive (EC) 32/2002 on undesirable substances in animal feed also sets a maximum level of 2.5 mg/kg in animal feed.
YOUR PLUS: AGROLAB Ibérica (Tarragona) has developed a simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of melamine in all types of food and feed by LC-MS/MS in positive electrospray ionisation mode (ESI+). The method is based on UNE-EN 16858 and has been validated with a wide range of matrices. This has enabled the scope of ISO 17025 accreditation for melamine analysis to be extended to all types of food and feed.
Autor: Dr. Frank Mörsberger; based on the Spanish article by Dra. Isabel Goméz

 Contact
Contact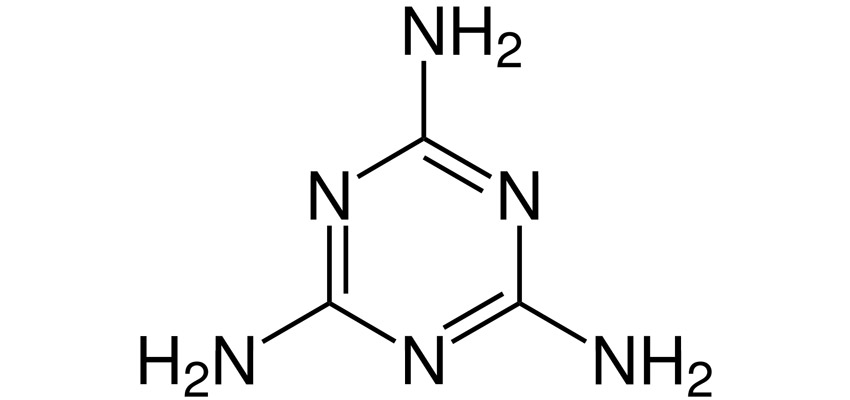

 Contact
Contact Career
Career