Pyrrolizidine alkaloids and tropane alkaloids are secondary plant constituents that are undesirable in food and feed due to their harmful potential.
Particularly in the case of tea, herbal teas, wild herbs (fresh and dried) as well as herbal food supplements, contamination with plant components containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids cannot always be ruled out with certainty. There are over 600 compounds in this natural substance class. Analytically, about 30 compounds are determined using a sensitive LC MS/MS method in our laboratory AGROLAB LUFA.
In the EU, maximum permissible amounts were set for some foodstuffs in 2020.
(see also AGROLAB RADAR issue JANUARY 2021).
Tropane alkaloids are found in solanaceae and bindweed, among others. The best-known representatives are atropine and scopolamine, which are also used pharmaceutically. In cereal fields, e.g. in organic farming, these plants can grow sporadically and their toxins can be carried into the cereal products. There have already been repeated product recalls of baby food (processed cereal foods), millet snacks and muesli mixtures due to high tropane alkaloids levels. For cereal-based foods for infants and young children containing millet, sorghum, buckwheat or products derived from them, maximum levels have been set in the EU. These are currently 1 ppm (1 µg/kg) each for atropine and scopolamine. We determine both substances in our alkaloid package.
NOTICE: have a look to the alert messages from RASFF below.
Interesting links to further information can be found below.
For Pyrrolizidine alkaloids:
https://www.agrolab.com/en/news/food-news/3124-mrl-pyrrolizidine-alkaloids.html
For Tropane alkaloids:
Author: Dr. Frank Mörsberger

 Contact
Contact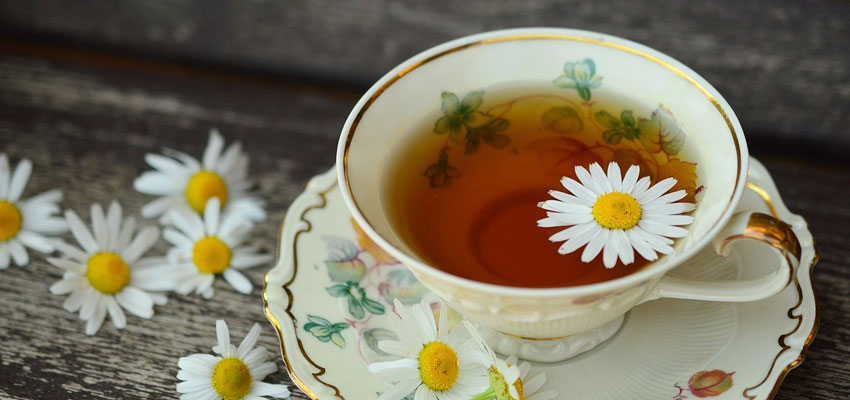

 Contact
Contact Career
Career