Purines are organic compounds and in the form of the purine bases adenine and guanine, they are important building blocks of DNA. Purines are mainly ingested in animal foods. However they are also found in pulses.
When the purines are metabolised in the body, uric acid is formed at the end. If the purine intake is too high, the uric acid can no longer be completely excreted by the body. The smallest uric acid crystals are deposited mainly in the joints and connective tissues, where they lead to very painful inflammations and tissue changes - popularly known as "gout nodules". Damage to the bladder and kidneys can also be caused by excessive uric acid concentrations.
For people and pets with elevated uric acid levels in the blood, a low-purine diet is usually recommended by doctors. For many foods, data on purine content can be found in corresponding diet tables (see links).
YOUR PLUS: The analysis of purines is currently particularly relevant in the area of pet food. We offer accredited analysis in this area. If required, we can also offer validated and accredited matrices in the food sector.
Read more in our product info: Product info Purine
Link:
Author: Dr. Frank Mörsberger

 Contact
Contact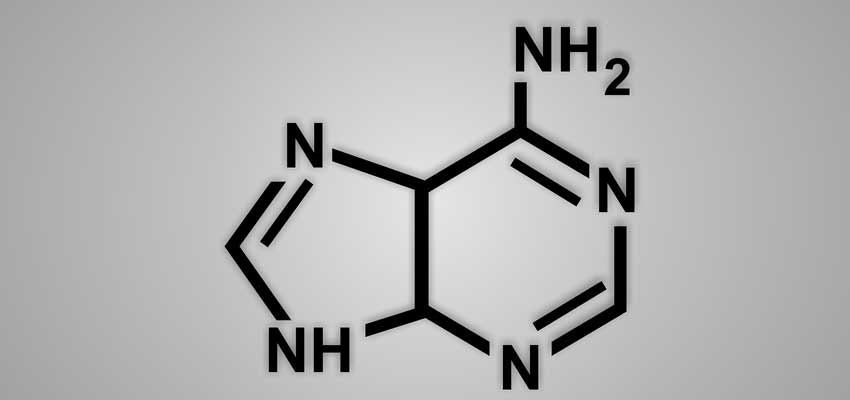

 Contact
Contact Career
Career